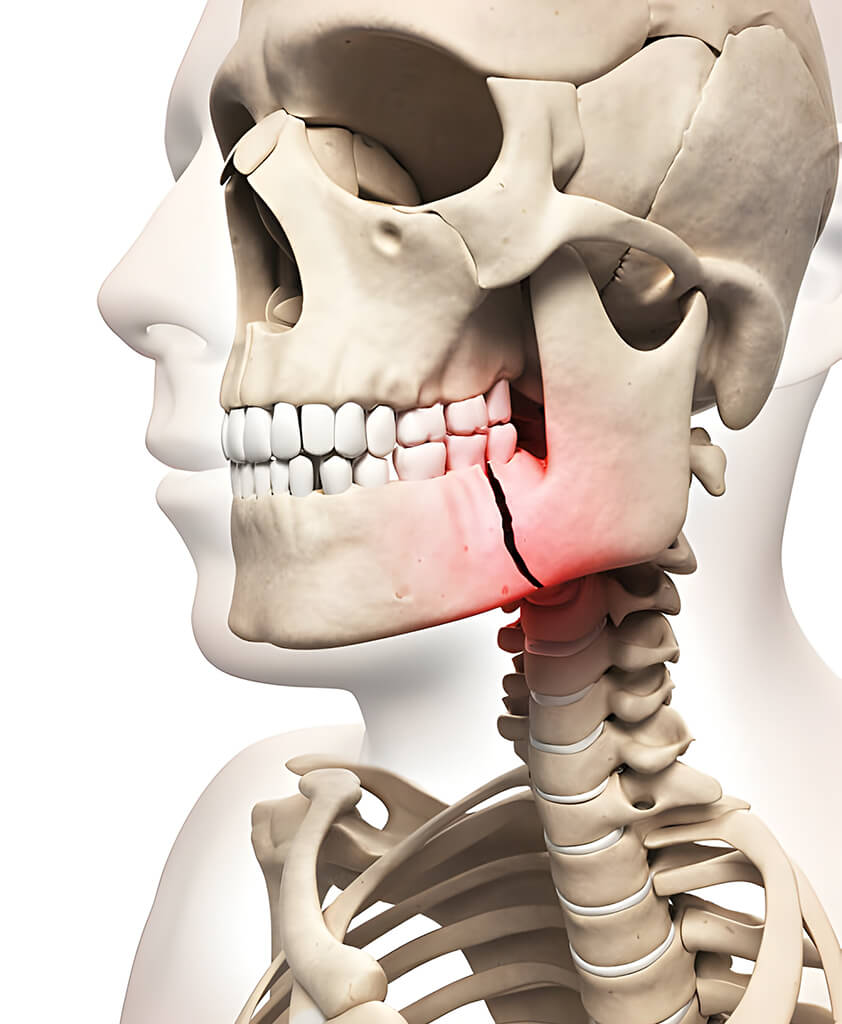
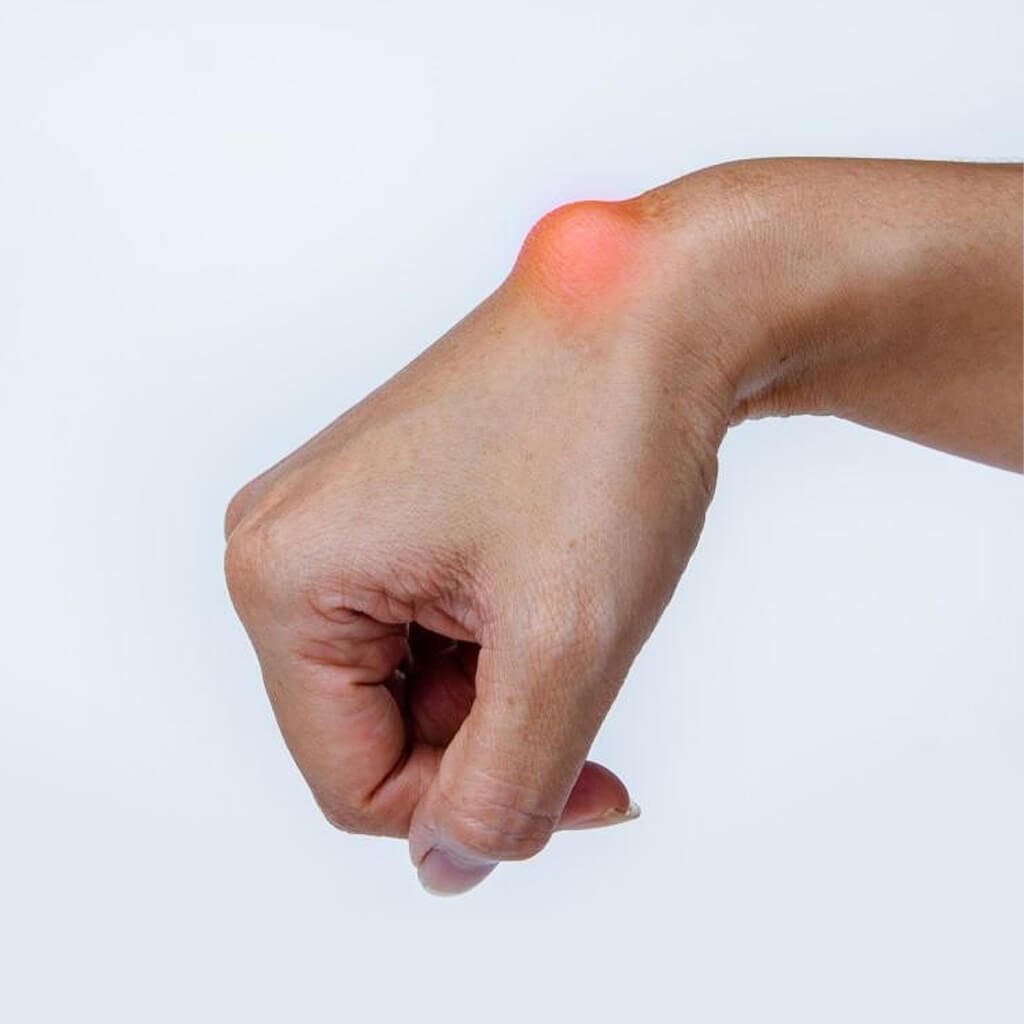
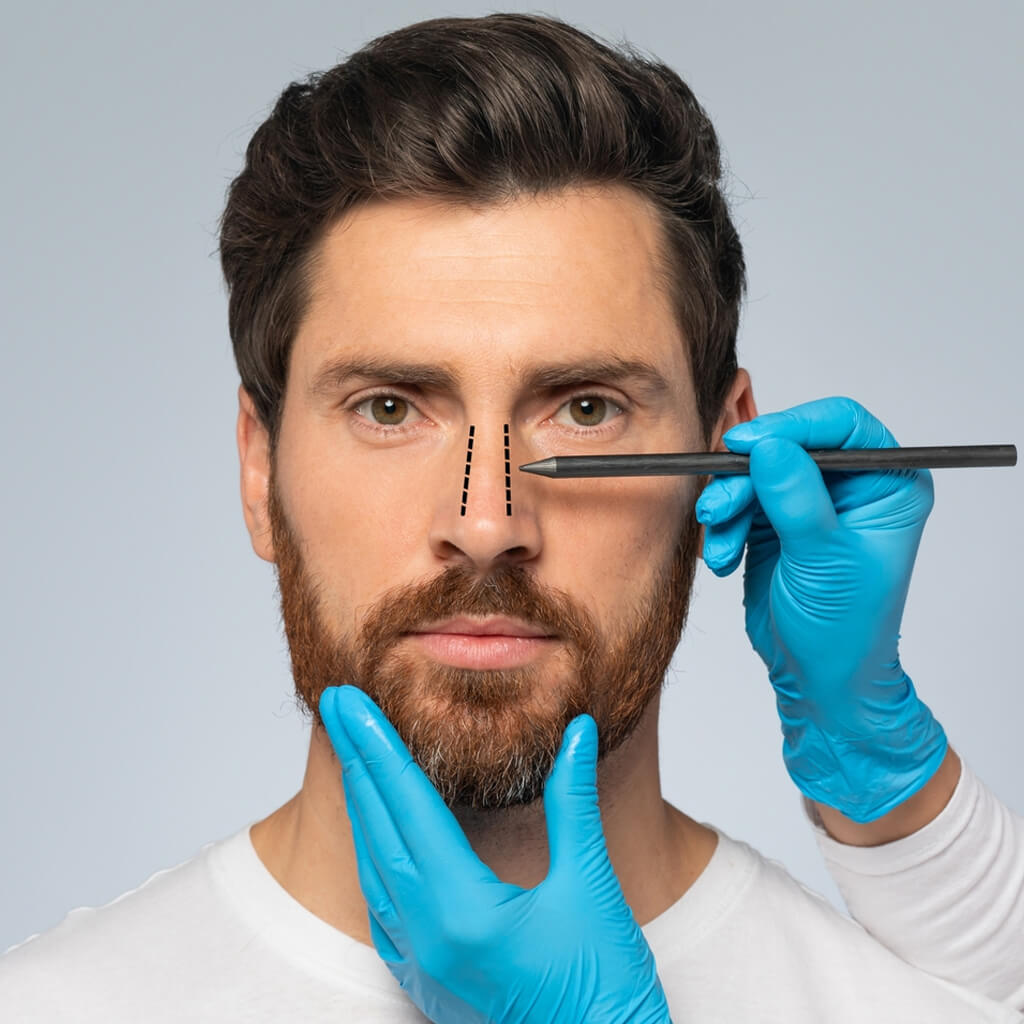
A facial bone fracture is a break in the nose, cheekbone, jaw, or eye socket caused by trauma or accidents. Dr. Anubhav Gupta offers advanced facial fracture treatment in Delhi to restore facial symmetry, function, and natural appearance. Early care ensures faster recovery and lasting results.